Plot Ranges of Data¶
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pyam
Read in some example data
fname = 'data.csv'
df = pyam.IamDataFrame(fname, encoding='ISO-8859-1')
df = (df
.filter({'variable': 'Emissions|CO2'})
.filter({'region': 'World'}, keep=False)
)
print(df.head())
Out:
model scenario region variable unit year value
9 MESSAGE-GLOBIOM SSP2-26 R5ASIA Emissions|CO2 Mt CO2/yr 2005 10488.011
15 MESSAGE-GLOBIOM SSP2-26 R5LAM Emissions|CO2 Mt CO2/yr 2005 5086.483
12 MESSAGE-GLOBIOM SSP2-26 R5MAF Emissions|CO2 Mt CO2/yr 2005 4474.073
3 MESSAGE-GLOBIOM SSP2-26 R5OECD Emissions|CO2 Mt CO2/yr 2005 14486.522
6 MESSAGE-GLOBIOM SSP2-26 R5REF Emissions|CO2 Mt CO2/yr 2005 2742.073
In this example, we want to show the range of a given dataset. We do this utilizing the fill_between argument.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
df.line_plot(ax=ax, color='variable', fill_between=True)
plt.show()
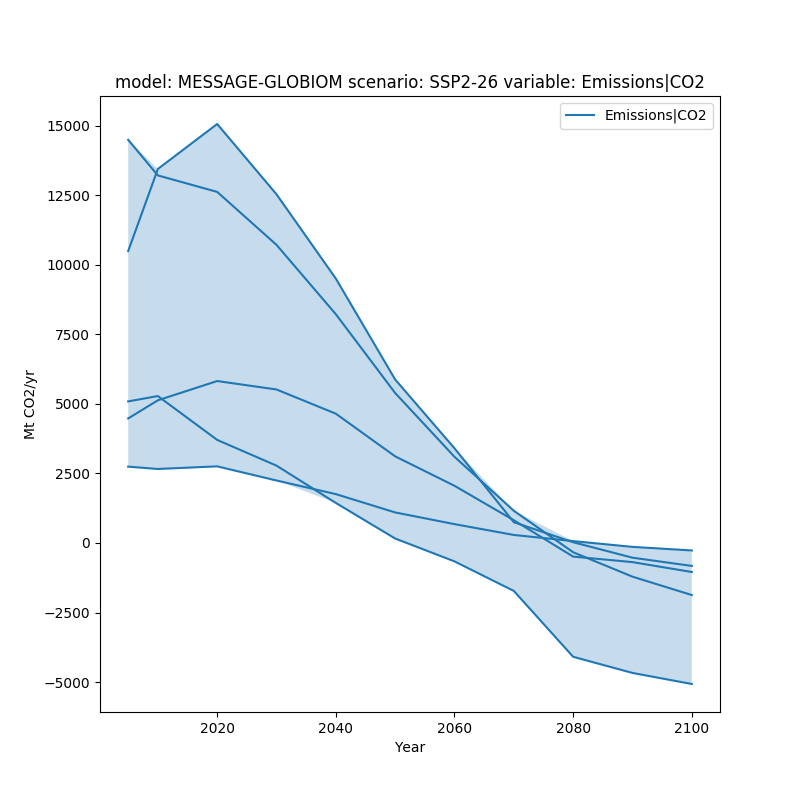
fill_between can simply be true, or it can be provided specific arguments as a dictionary.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
df.line_plot(ax=ax, color='variable', fill_between=dict(alpha=0.75))
plt.show()
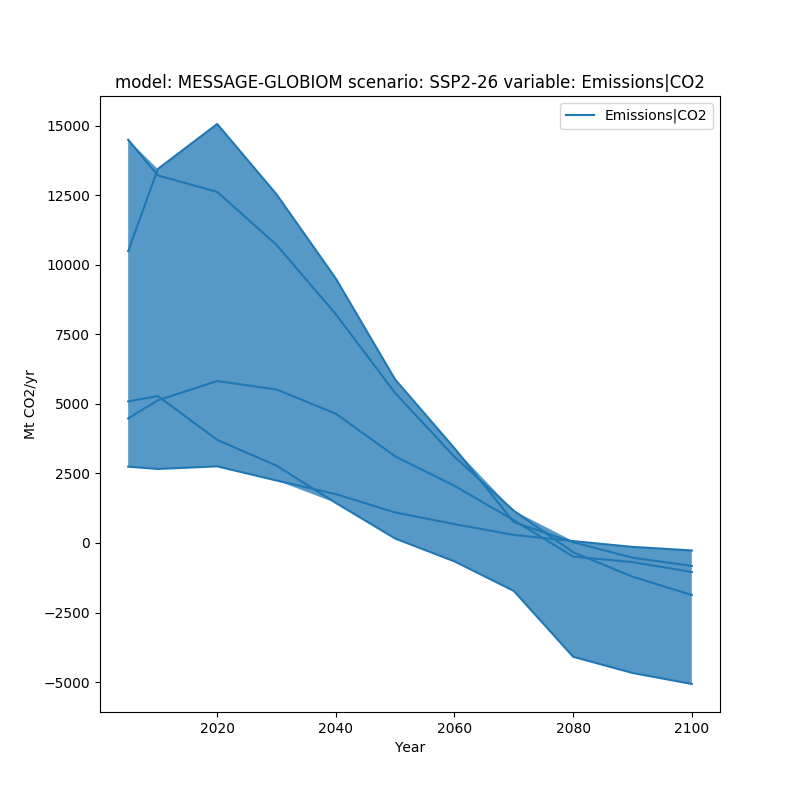
To further make the range of data visible, we can also add a bar showing the range of data in the final time period using final_ranges. Similar to fill_between it can either be true or have specific arguments.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
df.line_plot(ax=ax, color='variable', fill_between=True,
final_ranges=dict(linewidth=5))
plt.show()
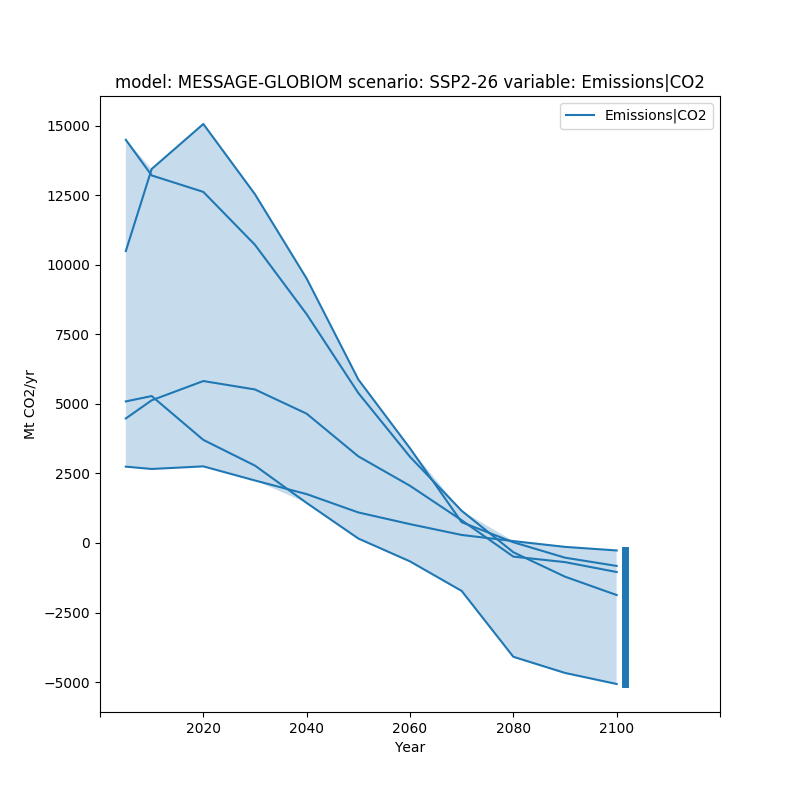
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.470 seconds)